Yes, IV therapy helps with hydration by delivering fluids directly into the bloodstream. This method bypasses the digestive system and provides faster results than drinking water. Medical professionals use IV hydration for severe dehydration, illness recovery, and specific health conditions.
IV therapy contains saline solution with electrolytes like sodium and potassium. The treatment takes 30-90 minutes and costs $75-400 per session. Healthy people rarely need IV hydration because drinking water provides adequate hydration for daily needs.
The global IV hydration therapy market was valued at $2.32 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $4.23 billion by 2030. This growth reflects increased awareness of hydration treatments, though medical experts question the necessity for wellness applications in healthy individuals.
What Is IV Therapy For Hydration?
IV therapy delivers fluids directly into veins through a small catheter. Medical professionals insert a thin tube into the arm or hand, connecting it to a bag of sterile solution.
Components Of IV Solutions
The IV solution contains normal saline, which is salt water that matches the body’s natural fluid balance. Healthcare workers add electrolytes including sodium, potassium, and chloride to restore proper mineral levels. Some treatments include vitamins and minerals based on specific patient needs.
Healthcare workers monitor the flow rate to prevent complications. The body absorbs 100% of IV fluids compared to 70-80% absorption from drinking water. This complete bioavailability explains why IV therapy works faster than oral rehydration methods.
IV Equipment And Procedure
Modern IV therapy uses sterile equipment following FDA guidelines for safety. Licensed medical professionals handle all aspects of treatment from insertion to monitoring. The procedure requires proper training and medical oversight to prevent complications.
IV bags hang from poles above patients, allowing gravity to create steady flow rates. Medical staff adjust the drip rate based on patient weight, age, and hydration needs. Treatment sessions typically last 30-90 minutes depending on fluid volume and individual response.
Does IV Therapy Work Faster Than Drinking Water?
IV therapy works faster than drinking water because it bypasses digestion. Oral fluids must pass through the stomach and intestines before reaching the bloodstream. IV fluids enter circulation immediately through direct vein access.
Absorption Speed Comparison
Absorption comparison shows IV fluids take 15-30 minutes for full effect while drinking water requires 2-4 hours for complete absorption. Research from Sports Medicine journal shows IV rehydration restores fluid balance 3 times faster than oral methods in athletes.
The University of Queensland studies confirm IV therapy provides more rapid rehydration in clinical settings. Athletes who received IV fluids showed improved performance markers within 30 minutes compared to 2-3 hours for those drinking sports drinks.
Physiological Limitations Of Oral Hydration
When people drink large amounts of water quickly, the kidneys filter out excess fluid before cells can absorb it. This protective mechanism prevents water poisoning but limits how fast oral hydration can work. IV therapy delivers controlled amounts directly to cells that need fluid replacement.
The digestive system has natural limits on fluid absorption rates. The small intestine can only process certain volumes per hour, creating bottlenecks during rapid rehydration attempts. IV therapy eliminates this limitation by delivering fluids straight to the circulatory system.
Who Actually Needs IV Hydration Therapy?
People with severe dehydration or inability to drink fluids need IV hydration. Medical conditions that require IV therapy include gastroenteritis, heat exhaustion, and post-surgical recovery.
Medical Conditions Requiring IV Hydration
Patients experiencing persistent vomiting cannot maintain adequate fluid intake through oral methods. The stomach rejects liquids, preventing normal hydration pathways from working. IV therapy provides necessary fluid replacement when oral intake becomes impossible.
Severe diarrhea causes rapid fluid loss that exceeds the body’s ability to replace through drinking. Cholera patients, for example, can lose several liters of fluid per day. IV therapy becomes essential for survival in these extreme cases.
Hospital And Clinical Applications
Hospital patients receive IV hydration when oral intake becomes impossible. Surgery patients cannot eat or drink for specific periods, requiring IV fluid support to maintain proper hydration levels during procedures and recovery.
Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy often require IV fluids due to nausea and reduced appetite. Treatment side effects prevent normal eating and drinking, making IV hydration necessary for maintaining basic physiological functions.
According to Cleveland Clinic data, over 200 million liters of IV saline are administered annually in US hospitals alone. This volume demonstrates the widespread medical necessity for IV hydration in clinical settings.
Emergency Medical Situations
Emergency departments use IV hydration for heat stroke victims who cannot regulate body temperature through normal cooling mechanisms. These patients need rapid fluid replacement to prevent organ damage and restore normal physiological function.
How Fast Does IV Hydration Take Effect?
IV hydration begins working within 15-30 minutes of starting treatment. Mild dehydration improves in 30 minutes, while severe cases need 2-4 hours for complete restoration.
Treatment Timeline By Severity
Timeline for different severity levels varies based on initial fluid deficit. Mild dehydration requires 30-60 minutes for symptom relief. Moderate dehydration needs 1-2 hours for complete restoration. Severe dehydration may require 2-4 hours of continuous treatment.
Factors Affecting Response Speed
Patient weight affects treatment duration because larger individuals have greater total body water volumes. A 200-pound person needs more fluid replacement than a 120-pound person to achieve the same hydration improvement.
Age influences how quickly the body responds to IV hydration. Older adults may require longer treatment times due to reduced kidney function and slower fluid distribution throughout body tissues.
Overall health status impacts response speed. People with heart or kidney problems may need slower infusion rates to prevent complications. Medical conditions can affect how efficiently the body processes and distributes IV fluids.
Monitoring During Treatment
Blood tests help medical professionals monitor treatment progress. Electrolyte levels, kidney function markers, and other indicators guide decisions about fluid type and infusion rates during therapy.
Patients typically feel improvement in energy levels and mental clarity within the first 30 minutes of treatment. Headaches from dehydration often resolve quickly as brain cells receive adequate fluid supply through restored circulation.
What Are The Benefits Of IV Therapy For Hydration?
IV therapy provides 100% fluid absorption and immediate results. The treatment bypasses digestive issues that prevent oral rehydration from working effectively.
Complete Bioavailability
Complete bioavailability means none of the administered fluid is wasted through digestive processes or kidney filtration before reaching cells. This efficiency allows smaller volumes to achieve better hydration results compared to drinking large amounts of water.
Rapid symptom relief occurs because fluids reach dehydrated tissues immediately through blood circulation. Patients experience improved energy, reduced headaches, and better mental clarity within minutes of starting treatment.
Customization Options
IV solutions can be customized with specific electrolytes and vitamins based on individual needs. Athletes use IV therapy to restore fluid balance after intense training sessions that cause significant sweat loss.
Studies published in the Journal of Athletic Training demonstrate faster recovery times with IV hydration compared to sports drinks in professional football players. 75% of NFL teams use IV prehydration for preventing muscle cramps during games.
Medical Advantages
Medical customization allows healthcare providers to address specific deficiencies identified through blood tests. Patients with low sodium levels receive different IV formulations than those with magnesium deficiencies.
The controlled delivery rate prevents overwhelming the cardiovascular system while providing steady rehydration. Medical professionals can adjust flow rates based on patient response and underlying health conditions.
IV therapy works regardless of digestive system problems that might interfere with oral rehydration. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease or other gastrointestinal conditions can receive effective hydration through IV methods.
What Are The Risks Of IV Hydration?
IV therapy carries risks including infection, vein damage, and fluid overload. Complications occur in less than 5% of treatments when performed by qualified medical professionals.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects include bruising at injection sites, affecting 10-15% of patients. Temporary discomfort during needle insertion is normal and resolves quickly. Some people experience coolness as room-temperature IV fluids enter body circulation.
Serious Complications
Serious complications include bloodstream infection, occurring in less than 0.1% of cases. Proper sterile technique and equipment sterilization prevent most infection risks. Licensed medical professionals follow strict protocols to maintain safety standards.
Blood clots can form in treated veins, though this complication remains rare with proper technique. Vein inflammation may occur if the catheter remains in place too long or if irritating solutions are used inappropriately.
Heart strain from excess fluid represents a serious risk for patients with cardiovascular disease. Rapid fluid administration can overwhelm the heart’s pumping capacity, leading to pulmonary edema or other complications.
Prevention And Safety Measures
Harvard Medical School research indicates most IV therapy complications result from improper technique or unsterile conditions. Choosing qualified providers with appropriate medical supervision reduces complication risks significantly.
Air embolism represents a rare but potentially fatal complication if air bubbles enter the bloodstream. Modern IV equipment includes safety features to prevent air from entering the system during treatment.
Electrolyte imbalances can occur if inappropriate IV solutions are used or if underlying medical conditions are not considered. Blood tests before treatment help prevent these complications through proper solution selection.
How Much Does IV Hydration Cost?
IV hydration costs $75-400 per session at wellness clinics depending on treatment type and location. Hospital IV therapy costs more but insurance covers medically necessary treatments.
Pricing Breakdown
- Basic saline IV treatments cost $75-150 • Vitamin-enhanced formulations range from $200-400
Emergency department IV hydration for severe dehydration typically costs $500-1500 but qualifies for insurance coverage when medically indicated.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance covers IV therapy for medical conditions like severe dehydration or post-surgical care. Documentation of medical necessity is required for coverage approval. Wellness IV treatments for hangovers or energy boosts are not covered by most insurance plans.
Cost-Saving Options
Membership programs at wellness clinics offer discounted rates for regular IV therapy users. Some facilities provide package deals that reduce per-session costs for clients who commit to multiple treatments.
Geographic location significantly affects pricing. Urban markets with higher operating costs typically charge more than rural areas. Premium locations in affluent neighborhoods often have higher prices for similar services.
Concierge IV services that provide in-home treatments charge premium rates for convenience. These services typically cost 50-100% more than clinic-based treatments due to travel time and mobile equipment expenses.
Comparing costs to oral rehydration solutions reveals significant price differences. Sports drinks cost $1-3 and provide similar final hydration levels, though they work more slowly than IV therapy.
Does IV Therapy Work Better Than Sports Drinks?
IV therapy works faster than sports drinks but both achieve similar hydration levels after adequate time. Sports drinks take 2-3 hours to restore fluid balance while IV therapy works in 30-60 minutes.
Effectiveness Comparison
Research from the American Journal of Emergency Medicine shows no significant difference in final hydration status between IV fluids and oral rehydration solutions. The speed difference becomes irrelevant once proper hydration is achieved through either method.
Sports drinks contain electrolytes and carbohydrates that help with fluid absorption through the digestive system. These formulations are specifically designed to optimize oral rehydration for athletes and active individuals.
Practical Considerations
Cost comparison heavily favors sports drinks, which cost $1-3 compared to $100-300 for IV therapy. Healthy individuals can achieve adequate hydration through oral methods without medical intervention or significant expense.
Athletes who cannot tolerate oral fluids due to nausea or digestive issues may benefit more from IV therapy. Competition stress sometimes affects digestion, making IV hydration a practical alternative for performance optimization.
The convenience factor varies by situation. Sports drinks are readily available and require no medical supervision. IV therapy requires scheduling, medical oversight, and dedicated treatment time in clinical settings.
Performance Outcomes
For routine hydration maintenance, sports drinks and water provide sufficient fluid replacement. IV therapy becomes advantageous only when rapid results are essential or when oral intake is contraindicated.
Research shows that athletes achieve similar performance outcomes whether they rehydrate with IV fluids or appropriately formulated sports drinks. The method matters less than achieving proper hydration levels before and after exercise.
When Should Someone Choose IV Hydration?
Choose IV hydration when unable to drink fluids or experiencing severe dehydration. Medical supervision is required for safe administration and proper fluid selection based on individual health status.
Appropriate Medical Situations
Appropriate situations include persistent vomiting that prevents oral intake for more than 24 hours. The stomach’s inability to retain fluids creates a medical emergency requiring IV intervention to prevent dangerous dehydration.
Severe illness with rapid fluid loss from multiple sources may exceed oral rehydration capacity. Patients with both vomiting and diarrhea cannot replace fluids fast enough through drinking alone.
Pre-surgical patients who cannot eat or drink for extended periods require IV hydration to maintain proper fluid balance. Surgical procedures often require empty stomachs, making IV therapy necessary for hydration maintenance.
Athletic And Performance Applications
Athletes competing in extreme heat conditions may benefit from IV prehydration when oral methods prove insufficient. Marathon runners and endurance athletes sometimes use IV therapy for performance optimization in challenging conditions.
When To Avoid IV Therapy
Avoid IV hydration for routine wellness or mild dehydration that responds well to oral methods. Drinking water with electrolytes provides adequate hydration for healthy individuals at much lower cost and risk.
Medical professionals evaluate each patient’s hydration needs before recommending treatment. Blood tests, vital signs, and symptom assessment guide decisions about whether IV therapy is appropriate for specific situations.
What Types Of IV Fluids Are Used For Hydration?
Normal saline and lactated Ringer’s solution are the most common IV fluids for hydration therapy. Normal saline contains 0.9% sodium chloride in sterile water, matching the salt concentration of human blood.
Standard IV Solutions
Lactated Ringer’s solution contains multiple electrolytes including calcium and potassium along with sodium chloride. This formulation more closely matches the electrolyte composition of body fluids, making it appropriate for complex dehydration cases.
According to NCBI medical guidelines, normal saline treats general dehydration while lactated Ringer’s solution addresses electrolyte imbalances. Medical professionals select the appropriate solution based on blood test results and patient symptoms.
Specialized Formulations
Half-normal saline contains 0.45% sodium chloride and is used when patients need fluid replacement without excessive sodium. This solution works well for people with heart conditions who must limit sodium intake.
Dextrose solutions contain sugar along with saline to provide calories and energy during hydration therapy. These formulations help prevent low blood sugar in patients who cannot eat during treatment periods.
Specialized IV solutions may include vitamins, minerals, or medications based on specific medical needs. Cancer patients might receive IV fluids with anti-nausea medications to address chemotherapy side effects.
Selection Criteria
The choice of IV fluid depends on laboratory results showing current electrolyte levels and kidney function. Medical professionals consider underlying health conditions when selecting the most appropriate hydration solution.
Volume and concentration decisions are based on the degree of dehydration and patient tolerance. Severe dehydration may require larger volumes of fluid over longer treatment periods to achieve safe rehydration.
Are There Alternatives To IV Hydration?
Oral rehydration solutions provide effective hydration for most people who can tolerate drinking fluids. These drinks contain optimal ratios of salt, sugar, and water for maximum absorption through the digestive system.
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy successfully treats 90% of dehydration cases without IV intervention according to World Health Organization data. This method costs significantly less and avoids the risks associated with intravenous procedures.
Electrolyte replacement drinks offer convenient hydration for mild to moderate fluid deficits. These commercial products are readily available and require no medical supervision for use by healthy individuals.
Natural Alternatives
Coconut water provides natural electrolytes and has gained popularity as a hydration alternative. This natural option contains potassium and other minerals that support fluid balance in the body.
Homemade oral rehydration solutions can be prepared using simple ingredients like salt, sugar, and water. The World Health Organization provides specific recipes for creating effective rehydration drinks at home.
For patients interested in comprehensive wellness approaches, facilities offer various health and wellness services that support hydration through natural methods and lifestyle modifications.
Food-Based Hydration
Food sources contribute significantly to daily fluid intake. Fruits and vegetables with high water content help maintain hydration levels throughout the day without requiring special treatments or supplements.
The key is matching the hydration method to the severity of fluid deficit and individual circumstances. Mild dehydration responds well to oral methods while severe cases require medical intervention with IV therapy.
How Do Medical Professionals Determine IV Hydration Needs?
Medical professionals assess hydration status through physical examination, laboratory tests, and patient symptoms. Vital signs including blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature provide important clues about fluid balance.
Assessment Methods
Blood tests reveal electrolyte levels, kidney function, and other markers that guide IV fluid selection. Sodium, potassium, and chloride levels help determine which type of solution will best address specific deficiencies.
Physical signs of dehydration include dry mouth, decreased skin elasticity, and reduced urine output. Severe dehydration may cause confusion, rapid heartbeat, and low blood pressure requiring immediate IV intervention.
Patient Evaluation
Patient history helps identify risk factors and underlying conditions that affect hydration needs. Medical conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and kidney problems influence treatment decisions and fluid selection.
Weight loss from fluid deficit provides objective measurement of dehydration severity. A 2% body weight loss indicates mild dehydration while 5% or more suggests severe fluid deficit requiring aggressive treatment.
Urine tests show concentration levels that reflect hydration status. Dark, concentrated urine suggests dehydration while pale, dilute urine indicates adequate fluid levels.
Medical facilities like those offering medical weight loss programs often monitor hydration as part of comprehensive health assessments and treatment planning.
Treatment Monitoring
Monitoring during treatment includes regular vital sign checks and patient response assessment. Medical professionals adjust fluid rates based on how patients respond to initial treatment efforts.
What Role Does IV Therapy Play In Different Medical Conditions?
IV therapy serves different purposes across various medical conditions beyond simple dehydration. Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy often need IV hydration to manage treatment side effects and maintain kidney function.
Surgical Applications
Surgical patients receive IV fluids to replace losses during operations and maintain blood pressure stability. Anesthesia and surgical stress affect normal fluid regulation, making IV support necessary for safe recovery.
Emergency Medicine
Emergency medicine uses IV hydration for heat-related illnesses when oral rehydration cannot work fast enough. Heat stroke victims need rapid cooling and fluid replacement to prevent organ damage.
Chronic Disease Management
Gastrointestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease may require IV hydration when the digestive system cannot absorb oral fluids effectively. These conditions impair normal absorption mechanisms.
Kidney disease patients sometimes need IV fluids to support remaining kidney function, though care must be taken to avoid fluid overload. Treatment requires careful monitoring of fluid balance and electrolyte levels.
Athletic Medicine
Athletes use IV therapy for performance enhancement and recovery, though this practice remains controversial. The World Anti-Doping Agency prohibits IV infusions over 50 mL per 6 hours in competitive sports.
Pregnancy And Reproductive Health
Pregnancy complications may require IV hydration for conditions like hyperemesis gravidarum, where severe nausea prevents adequate oral intake. Treatment helps protect both mother and developing baby.
Facilities providing comprehensive care often integrate IV therapy with other treatments like hormone replacement therapy for optimal patient outcomes.
How Has IV Hydration Evolved In Wellness Settings?
IV hydration has expanded beyond medical necessity into wellness and lifestyle applications. Wellness centers now offer IV therapy for hangover recovery, energy enhancement, and general health optimization.
Market Development
Celebrity endorsements and social media promotion have increased public awareness of IV therapy benefits. High-profile individuals sharing their experiences with IV treatments have contributed to growing consumer interest.
Mobile IV services bring treatments directly to homes, offices, and events for convenience. These services cater to busy professionals and individuals seeking premium healthcare experiences.
Customization And Innovation
Customized IV formulations target specific wellness goals like immune support, athletic performance, and anti-aging. Providers create specialized blends of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients for different objectives.
The wellness IV market has grown rapidly, with projected revenues reaching billions of dollars. This growth reflects changing consumer attitudes toward preventive healthcare and wellness optimization.
Scientific Scrutiny
Scientific scrutiny of wellness IV claims has increased as the market expands. Medical professionals question the necessity and cost-effectiveness of IV therapy for healthy individuals.
Regulatory oversight varies by location, with some states requiring physician supervision while others allow broader practitioner involvement. This regulatory landscape affects treatment availability and safety standards.
Modern facilities offering IV therapy often combine treatments with other wellness services like vitamin shots to provide comprehensive health optimization programs.
What Does Research Say About IV Hydration Effectiveness?
Research shows IV hydration works faster than oral methods but questions remain about necessity for healthy individuals. Studies focus primarily on medical applications rather than wellness uses.
Clinical Evidence
Clinical trials demonstrate IV therapy effectiveness for treating severe dehydration in hospital settings. Emergency medicine research supports IV use for heat-related illnesses and gastroenteritis.
Athletic performance studies show mixed results regarding IV hydration benefits. Some research indicates faster recovery while other studies find no performance advantage over oral rehydration.
Research Limitations
Long-term safety data for regular IV therapy in healthy people remains limited. Most research examines short-term medical use rather than ongoing wellness applications.
Cost-effectiveness analyses consistently favor oral rehydration for situations where both methods work equally well. The speed advantage of IV therapy rarely justifies the increased expense and risk.
Psychological Factors
Placebo effects may contribute to positive experiences with wellness IV therapy. People often feel better after treatment regardless of objective physiological changes.
Quality research on IV therapy continues expanding as the wellness market grows. Future studies may provide better guidance on appropriate uses and frequency for healthy individuals.
Professional medical organizations generally support IV therapy for appropriate medical indications while questioning routine wellness applications. Evidence-based medicine emphasizes using treatments when benefits clearly outweigh risks.
What Should People Know Before Choosing IV Hydration?
People considering IV hydration should understand both benefits and risks before making treatment decisions. Medical consultation helps determine whether IV therapy is appropriate for specific situations and health conditions.
Pre-Treatment Considerations
Cost considerations include both direct treatment expenses and potential complication costs. Insurance coverage varies significantly based on medical necessity and specific circumstances.
Time commitment involves not just the treatment session but also travel to facilities and recovery time. Most sessions require 30-90 minutes plus additional time for consultation and monitoring.
Provider Selection
Provider qualifications matter significantly for safety and effectiveness. Licensed medical professionals should oversee all aspects of IV therapy from assessment through administration and monitoring.
Alternative methods like oral rehydration may achieve similar results at lower cost and risk. Healthy individuals should explore these options before pursuing IV treatments.
Health Assessment
Individual health status affects both treatment response and complication risks. People with heart, kidney, or other chronic conditions need careful medical evaluation before IV therapy.
Realistic expectations help avoid disappointment with treatment outcomes. IV therapy provides rapid hydration but cannot address underlying health problems or replace healthy lifestyle practices.
Professional facilities offering IV therapy should provide comprehensive consultations that include discussion of alternatives and realistic outcome expectations for each individual situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does IV Hydration Last?
IV hydration effects typically last 24-48 hours depending on activity level and fluid loss. The body naturally processes and eliminates excess fluids through normal kidney function.
Is IV Hydration Safe For Everyone?
IV hydration is not safe for everyone. People with heart disease, kidney problems, or certain medications need medical clearance before treatment. Healthy individuals face minimal risks when treated by qualified professionals.
Can IV Hydration Replace Drinking Water?
IV hydration cannot replace regular water consumption. The treatment addresses acute dehydration but daily hydration maintenance requires consistent fluid intake through drinking and eating.
How Often Can Someone Get IV Hydration?
Frequency depends on medical need and individual health status. Most wellness providers recommend waiting at least one week between sessions. Medical necessity may require more frequent treatments under doctor supervision.
Does IV Hydration Help With Weight Loss?
IV hydration does not directly cause weight loss. Some formulations may temporarily reduce appetite or provide energy, but sustainable weight management requires proper diet and exercise habits.
What Should I Expect During IV Treatment?
Expect a brief needle insertion followed by 30-90 minutes of fluid infusion. Most people experience minimal discomfort and can read or relax during treatment. Medical staff monitor throughout the session.
Are There Age Restrictions For IV Hydration?
Age restrictions vary by provider and treatment type. Most wellness clinics treat adults 18 and older. Medical IV hydration has no age limits when medically necessary under proper supervision.
Final Thoughts
IV therapy helps with hydration by delivering fluids directly to the bloodstream, providing faster results than oral methods. Medical necessity guides appropriate use for severe dehydration, surgical support, and specific health conditions.
Healthy individuals rarely need IV hydration because drinking water and oral rehydration solutions provide adequate fluid replacement. The speed advantage of IV therapy does not justify routine use for wellness purposes in most circumstances.
Cost, risk, and time considerations favor oral hydration methods for daily fluid maintenance. Reserve IV therapy for situations where medical professionals recommend it based on specific health needs and circumstances.
People considering IV hydration should consult qualified medical professionals to determine appropriate treatment options. Comprehensive health assessments help identify whether IV therapy offers meaningful benefits over less invasive alternatives.
Consider exploring other wellness options at facilities like those offering biorepeel treatments and peptide therapy that may support overall health and wellness goals through different approaches.


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/botox1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before3-150x150.png)



![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-4-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-5-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Eyebrow-treatment-1-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Rejuvenation-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Rejuvenation-2-150x150.png)


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Lip-Filler-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Before-1-150x150.jpg)


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-1-150x150.png)

![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Thread-Lifts-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Thread-Lifts-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Lip-Filler-2-150x150.png)
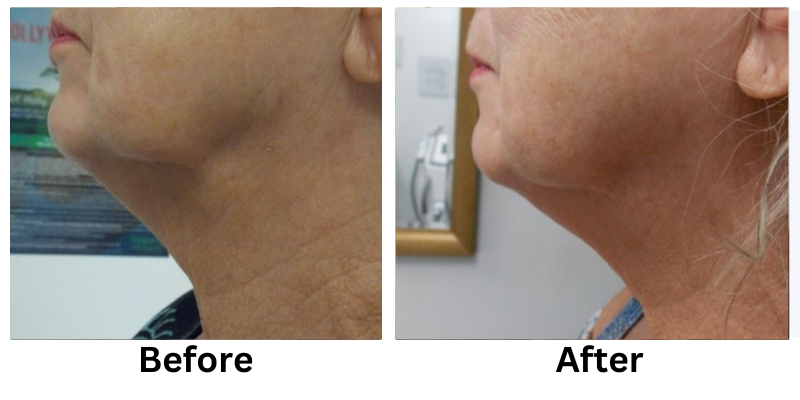
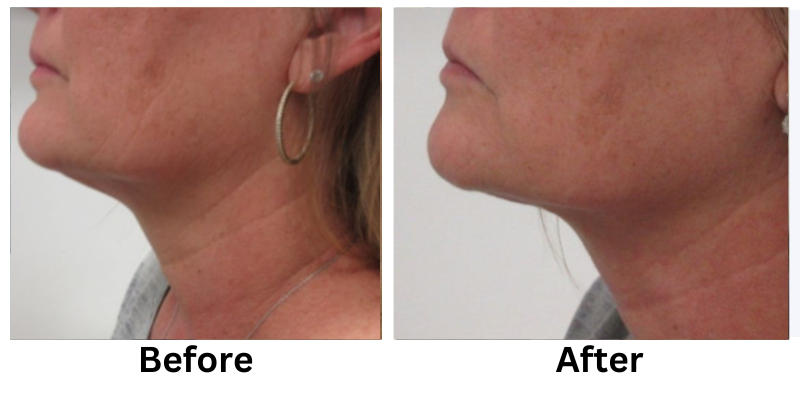

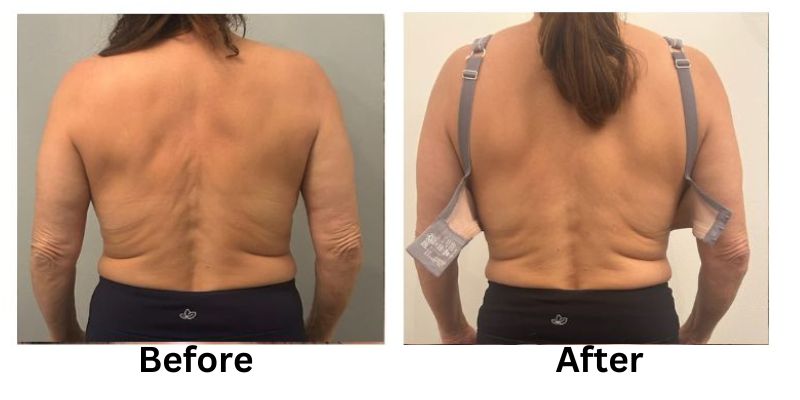
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/skin-reuvulation1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/skin-rejuvulation-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Tighting-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before-150x150.jpg)
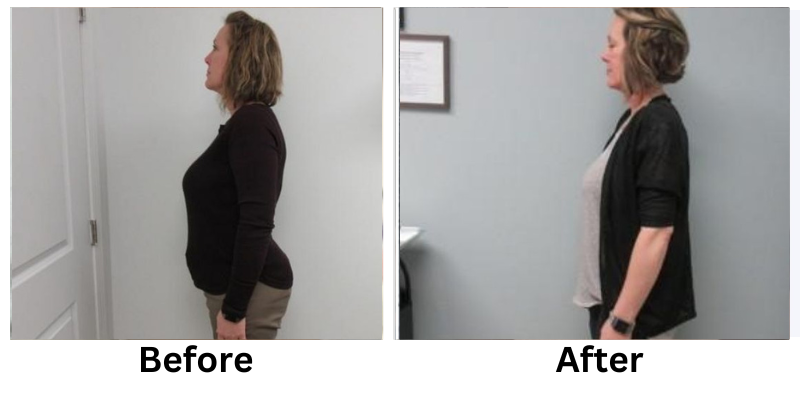



![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/weightloss-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/weightloss-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/2Weight-Loss-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Weight-Loss-1-new-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Weight-Loss-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Slimming-Solutions-BA-Template-150x150.png)


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat-0-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before-1-150x150.png)
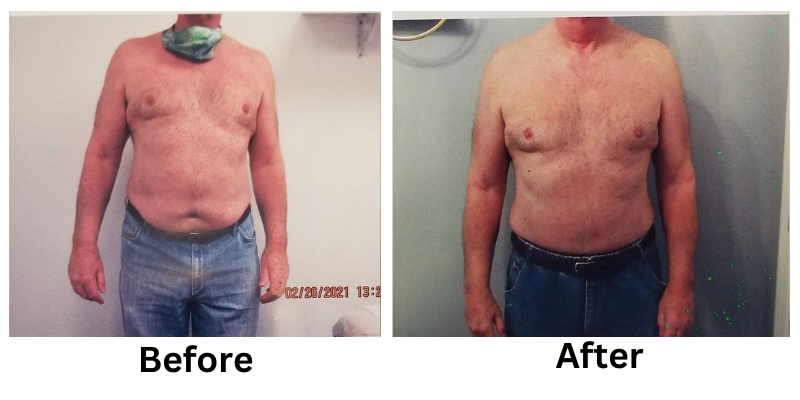

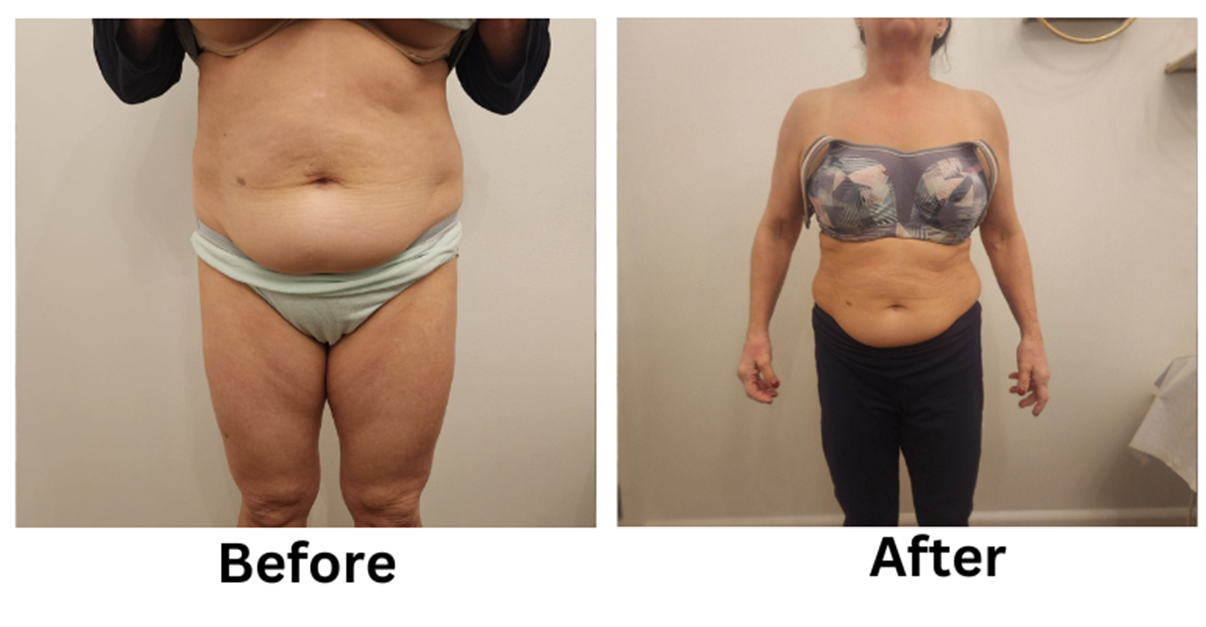
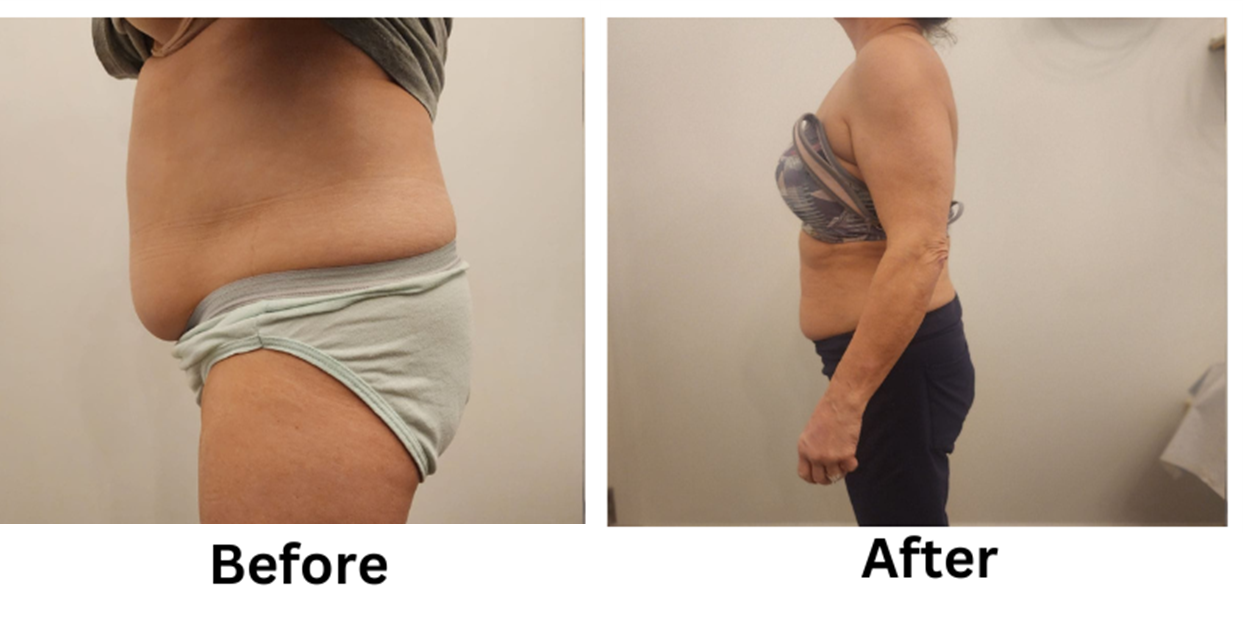
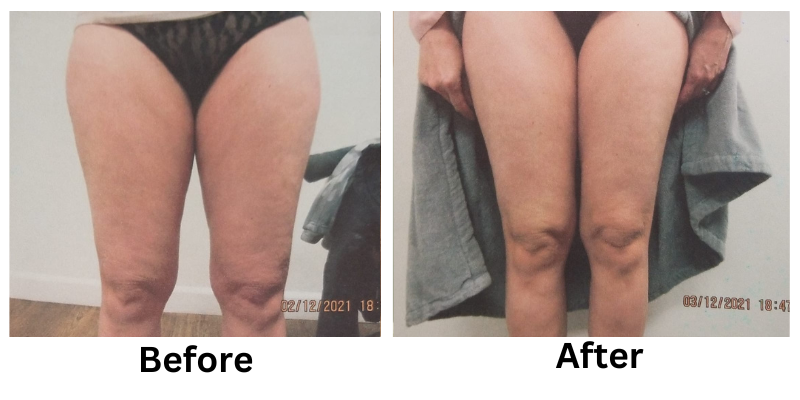
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ems-BNA-front-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/EMS-bna-SIDE-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-6-150x150.png)