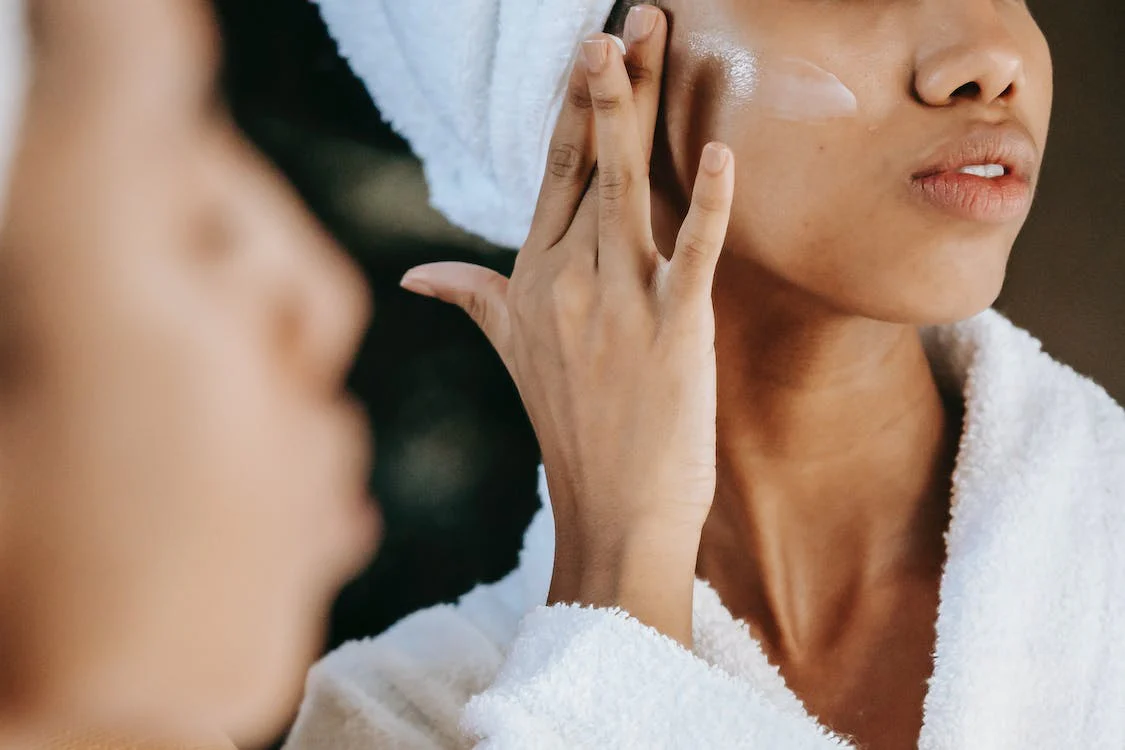
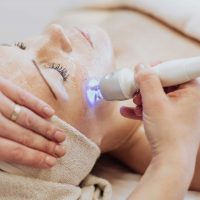
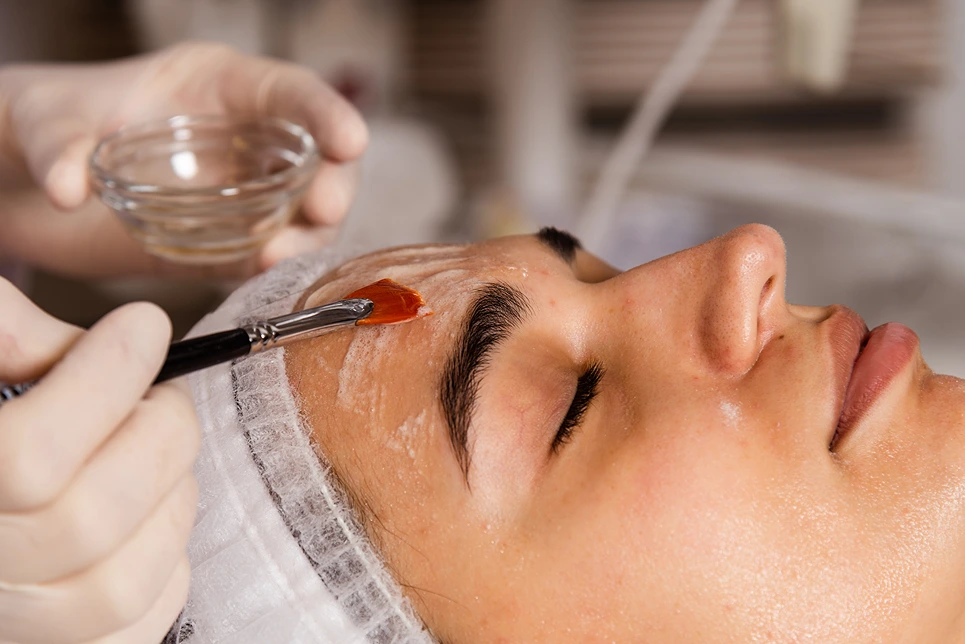
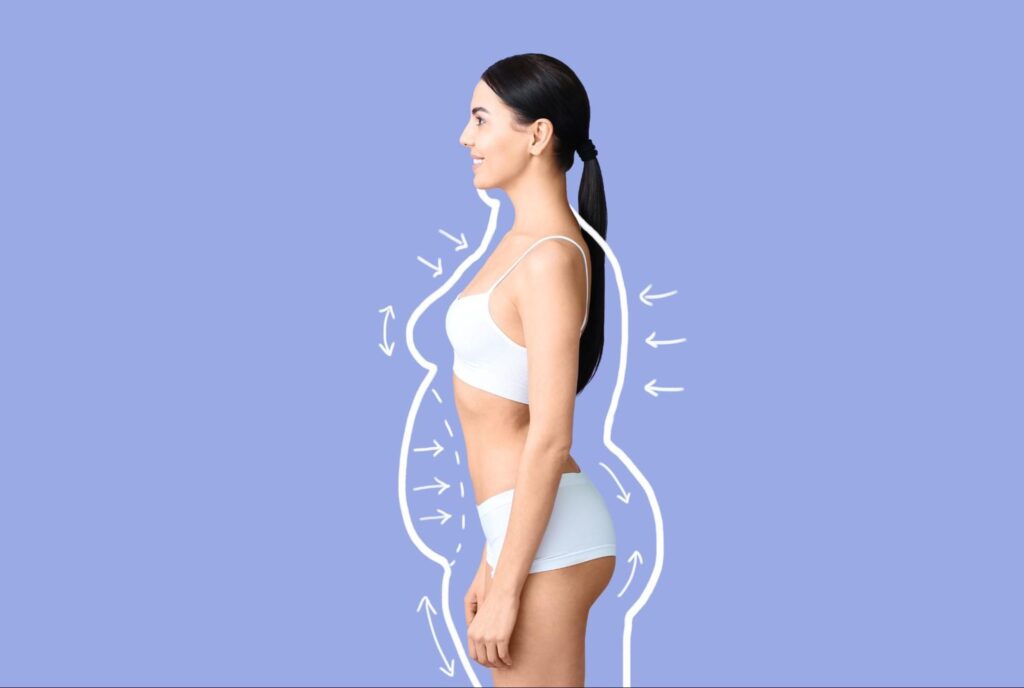
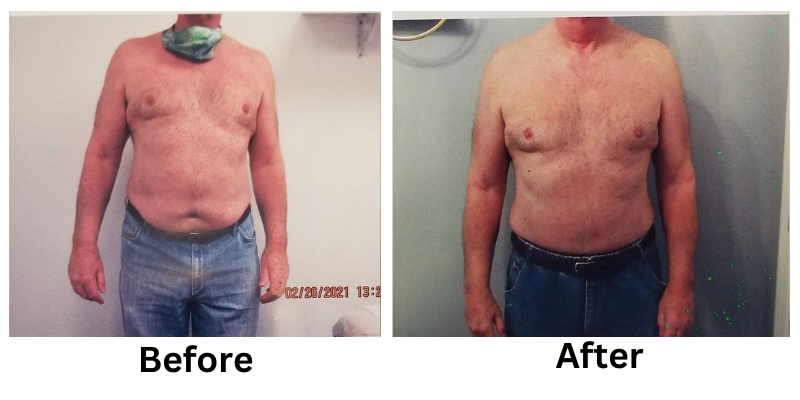
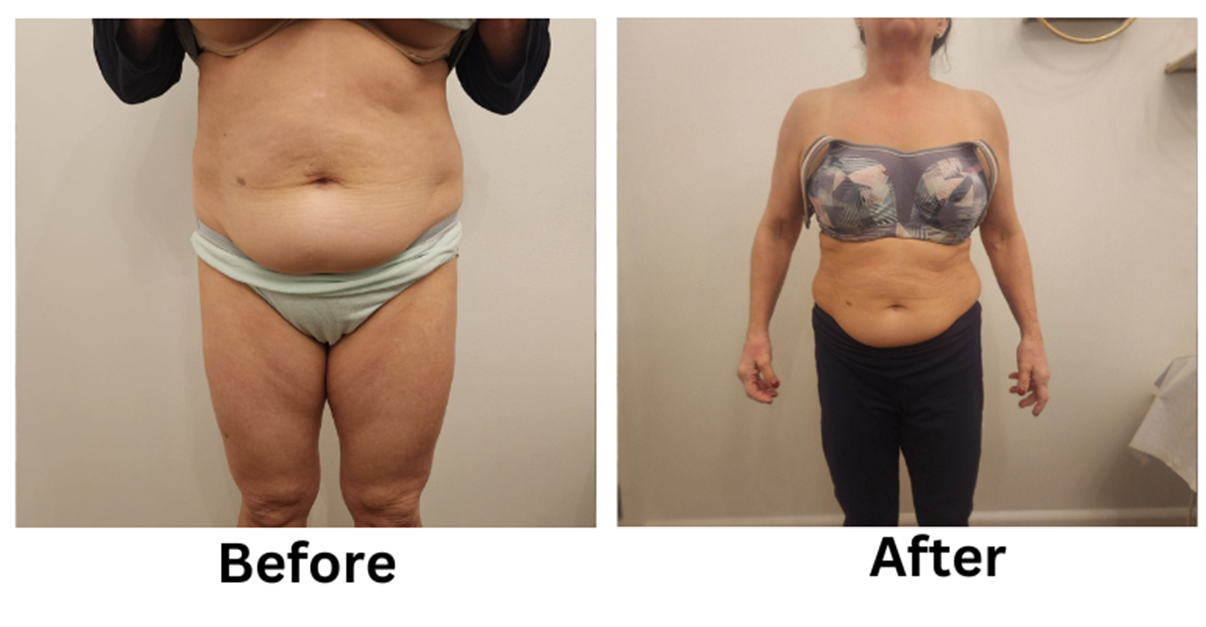
Non-invasive weight loss options like cryolipolysis, laser fat removal, and radiofrequency therapy reduce stubborn fat without surgery.
These methods are safe, require minimal downtime, and target specific areas for gradual, natural results. Pairing treatments with healthy lifestyle habits ensures long-term success.
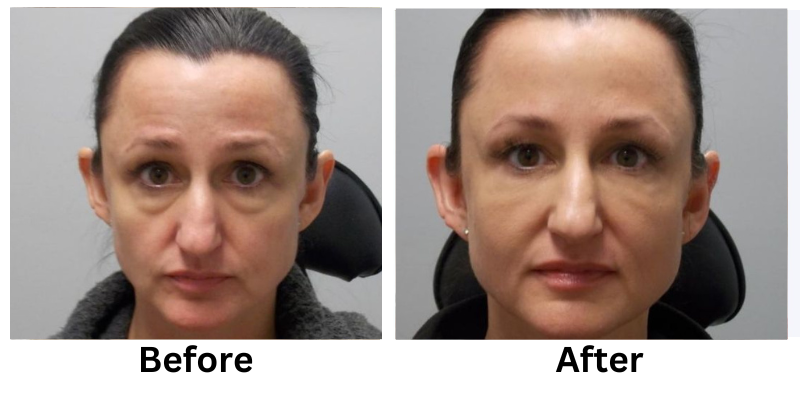
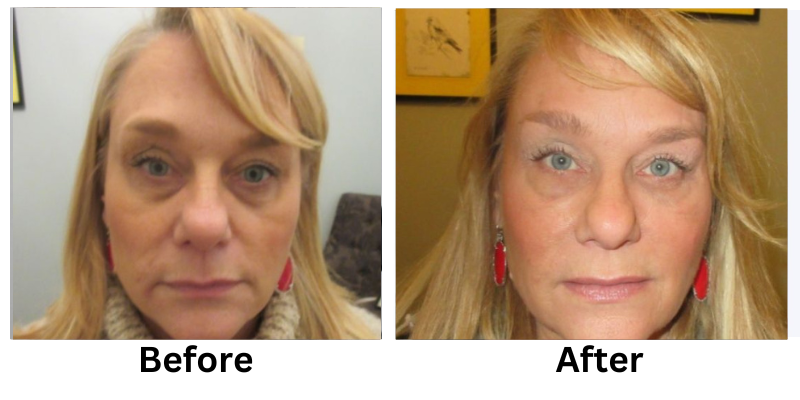
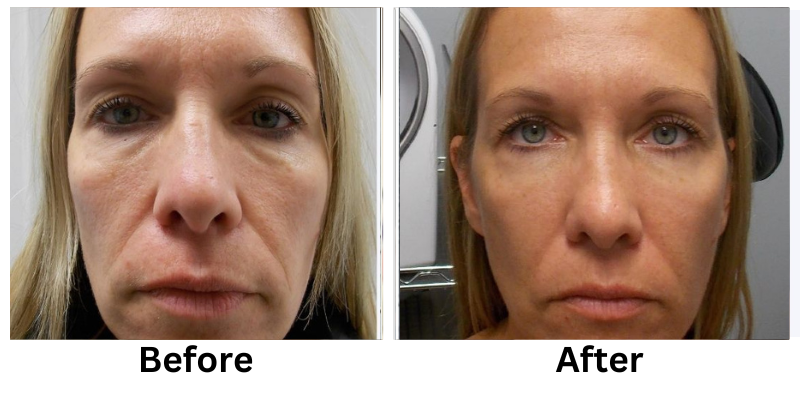
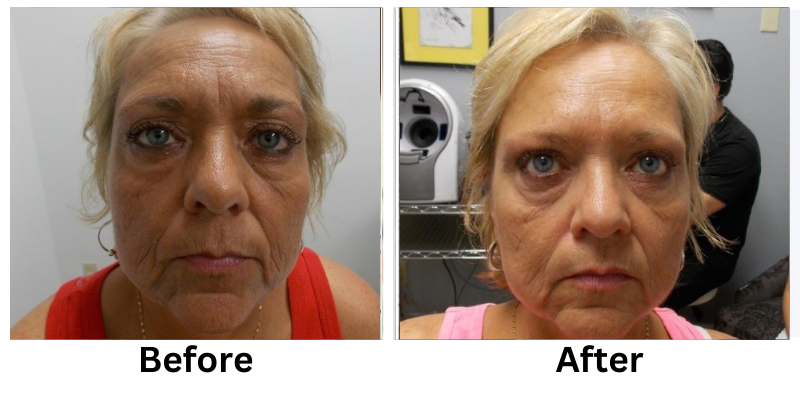
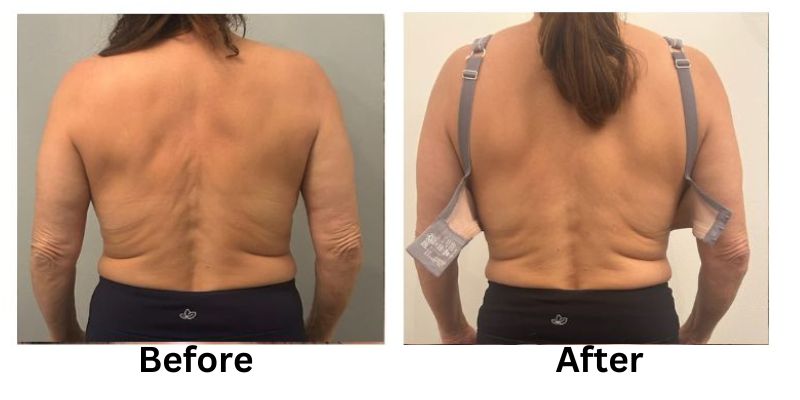
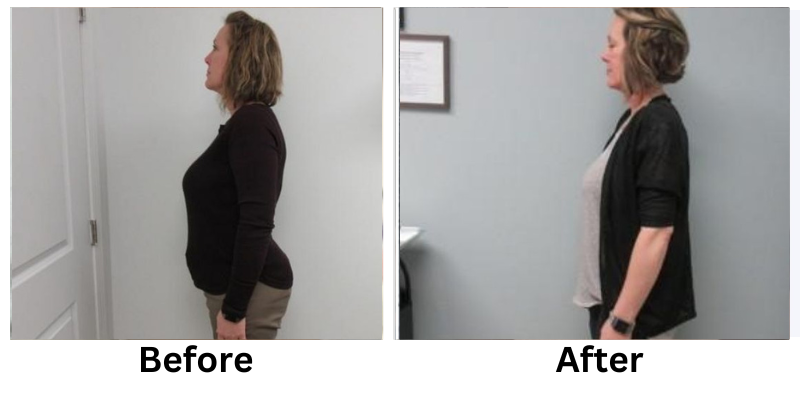
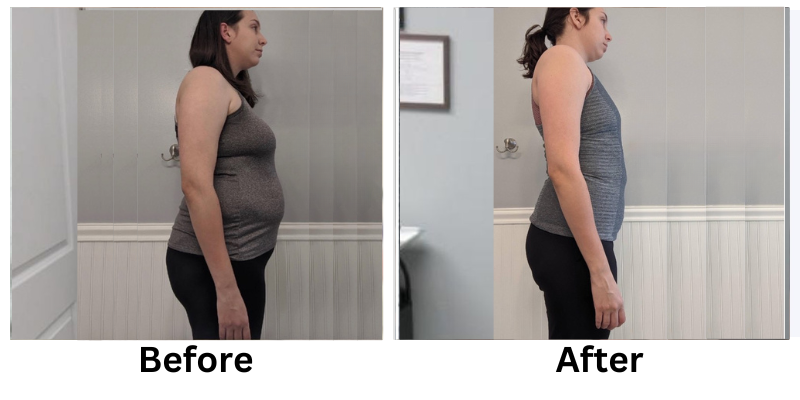
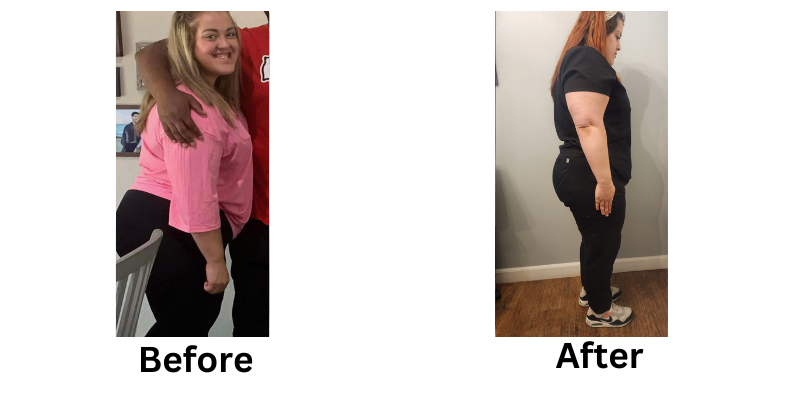
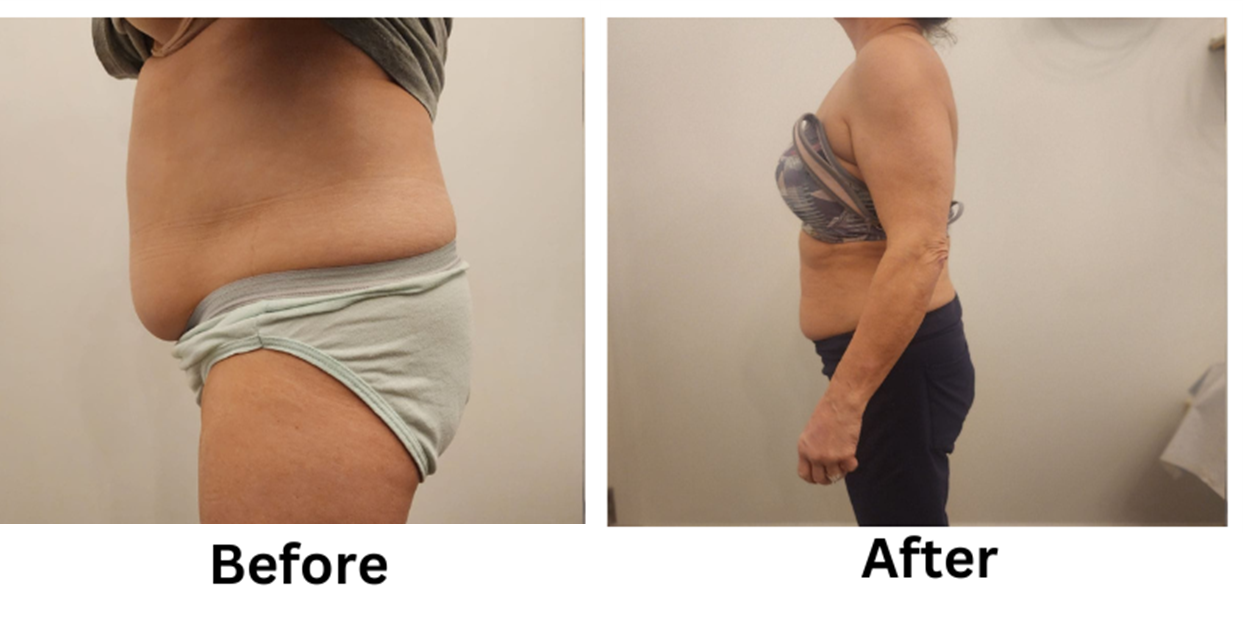
Losing weight can be a challenging process, but non-invasive weight loss options offer a safe and effective alternative to surgical methods. These treatments focus on reducing stubborn fat, improving body contours, and enhancing overall health without requiring incisions or extended recovery time.
By combining advanced technology with lifestyle changes, non-invasive methods provide a personalized approach to weight management.
Understanding Non-invasive Weight Loss
Non-invasive weight loss techniques target fat cells using innovative methods like freezing, heating, or sound waves. These treatments avoid the risks associated with surgery, such as scars or infections.
Procedures like cryolipolysis, laser fat removal, and ultrasound fat reduction allow individuals to focus on specific areas, delivering gradual and natural results. For those looking to complement their care, residential treatments provide tailored programs to enhance outcomes.
Benefits of Non-invasive Treatments
Non-invasive methods offer multiple advantages. They eliminate the need for anesthesia, significantly reduce downtime, and avoid surgical scars. These treatments are designed to focus on localized fat deposits, making it possible to achieve precise results.
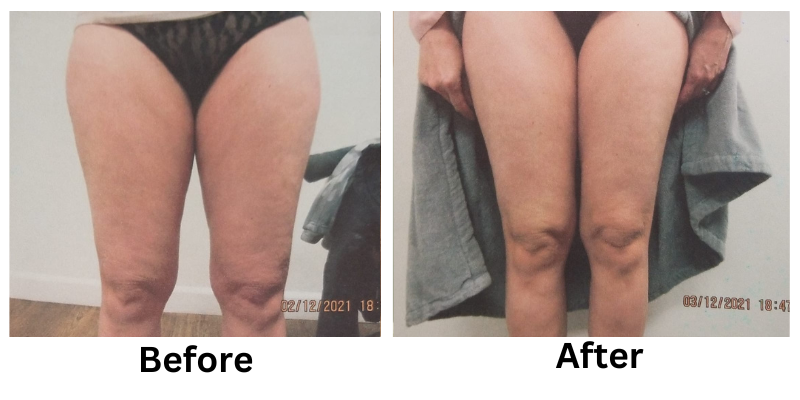
They are also safer compared to surgery, reducing risks while providing long-lasting changes. Additionally, non-invasive methods are versatile, addressing areas such as the abdomen, thighs, arms, and chin.
Popular Non-invasive Weight Loss Techniques
Cryolipolysis (Fat Freezing)
Cryolipolysis, also known as CoolSculpting, freezes fat cells in targeted areas like the abdomen and thighs. This FDA-approved procedure causes fat cells to break down naturally, leaving the surrounding tissue unaffected.
Over time, the body processes and removes the damaged fat cells, leading to visible improvements. A session typically lasts 35–60 minutes, and results appear within one to three months.
Laser Fat Removal
Laser fat removal uses low-energy lasers to break down fat cells, which are then metabolized by the body. This painless method is ideal for areas like the chin, upper arms, and abdomen.
Multiple sessions may be required to achieve the best results, with each session lasting 25–45 minutes. For additional care options, explore commercial treatments designed to complement these procedures.
Radiofrequency Therapy
Radiofrequency (RF) therapy uses heat to shrink fat cells while tightening the skin. It is an effective choice for reducing cellulite and addressing loose skin in areas like the stomach and thighs. Sessions typically last 30–60 minutes, with gradual results that improve over time.
Ultrasound Fat Reduction
Ultrasound therapy targets fat cells with sound waves, destroying them without affecting nearby tissue. This technique is painless and effective for larger areas such as the hips and stomach.
Results are usually seen over three to six months, as the body naturally eliminates the destroyed fat cells.
The Role of Lifestyle in Non-invasive Weight Loss
Non-invasive weight loss treatments are most effective when paired with healthy lifestyle habits. A balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables supports fat reduction and overall health.
Incorporating regular exercise, including strength training and cardio, can enhance results by boosting metabolism and preserving muscle tone.
Adequate hydration helps metabolize fat, while proper sleep ensures the body can effectively regulate hunger hormones. Combining these habits with treatments creates a sustainable weight loss plan.
Choosing the Right Non-invasive Treatment
The best treatment depends on individual goals and body type. Cryolipolysis works well for specific fat pockets, while radiofrequency therapy is ideal for reducing cellulite and tightening loose skin.
Laser fat removal is best for smaller areas like the chin, and ultrasound fat reduction suits larger regions. Consulting a certified professional ensures the most suitable approach, tailored to meet individual needs and achieve desired results.
Comparing Non-invasive and Surgical Weight Loss
Non-invasive techniques differ from surgical options like liposuction and bariatric surgery. Surgery provides immediate results but comes with higher risks, scarring, and lengthy recovery periods.
Non-invasive methods, by contrast, are safer and focus on gradual improvements. They are particularly beneficial for individuals close to their ideal weight who are looking to fine-tune their body shape.
Maintaining Long-term Results
Sustaining the benefits of non-invasive treatments requires commitment to healthy habits. Following a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, and staying hydrated are essential for maintaining results.
Periodic follow-up sessions, if recommended, can enhance outcomes further. Long-term success depends on a holistic approach that combines professional treatments with a well-rounded lifestyle.
Integrating Non-invasive Treatments With Professional Guidance
Non-invasive weight loss options are most effective when paired with expert care. Certified professionals provide customized plans that address individual needs, ensuring safe and optimal results.
Their expertise enhances the overall effectiveness of the chosen methods while minimizing risks. Combining professional guidance with a consistent routine at home ensures lasting success.
Non-invasive weight loss treatments offer a modern solution for reducing stubborn fat and improving body contours. From cryolipolysis to laser fat removal, these methods provide effective results without the risks of surgery.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and consulting with professionals, individuals can enjoy long-lasting benefits. Explore residential treatments and commercial treatments to discover tailored solutions that meet your needs.


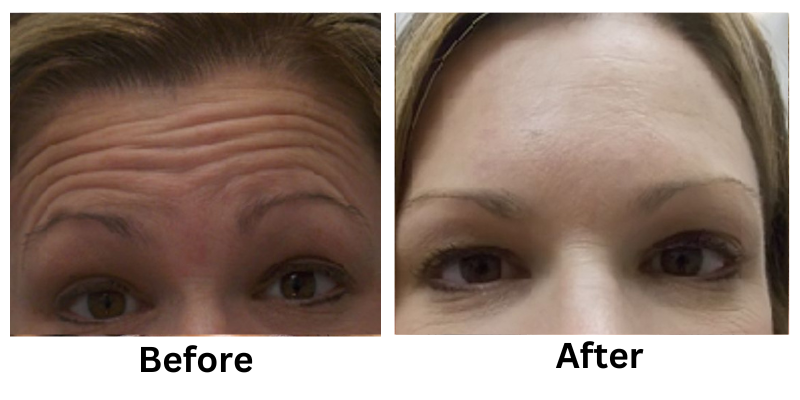
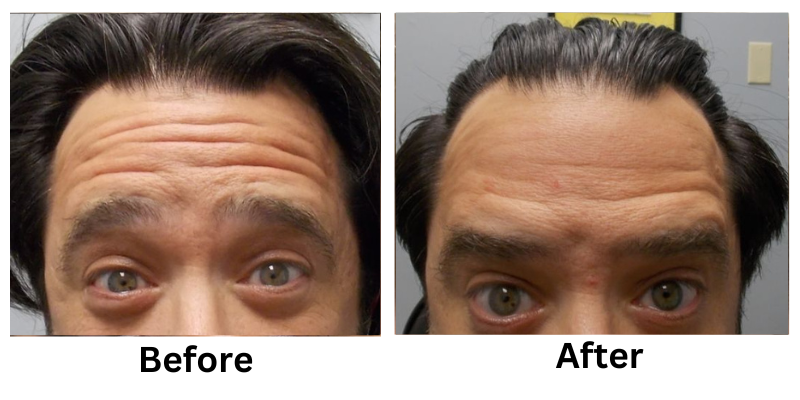
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/botox1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before3-150x150.png)


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Liquid-face-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Liquid-face-1-150x150.png)
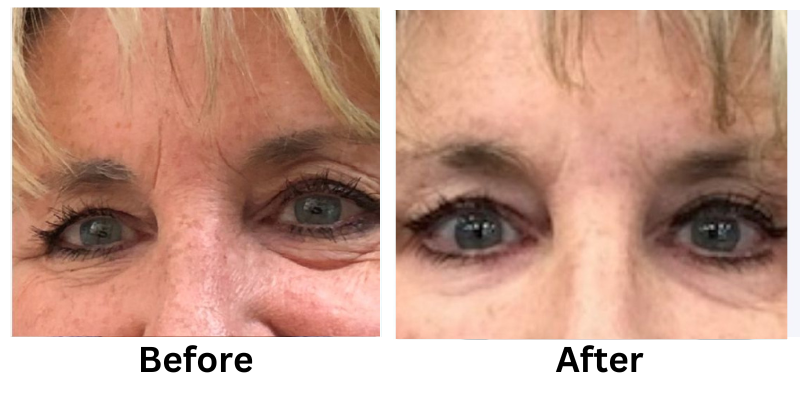
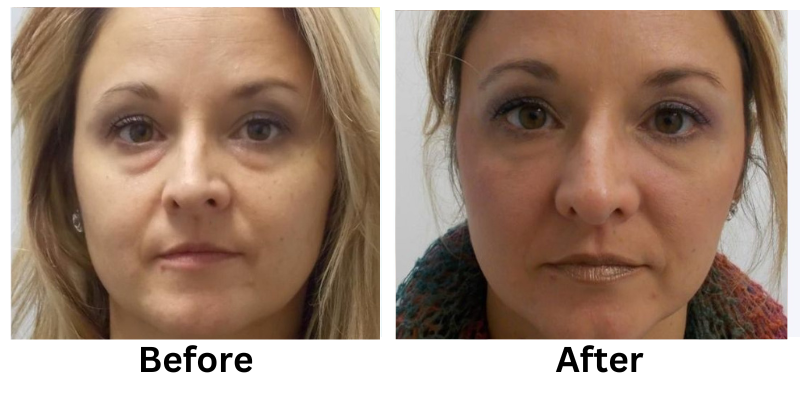


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-4-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/revanesse-versa-5-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Eyebrow-treatment-1-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Rejuvenation-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Rejuvenation-2-150x150.png)


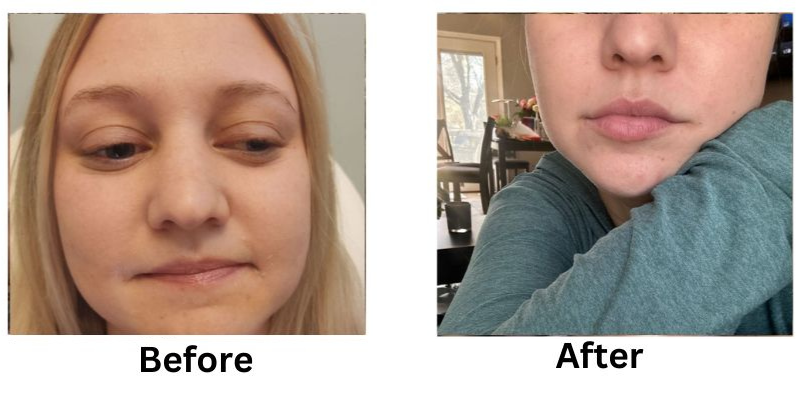
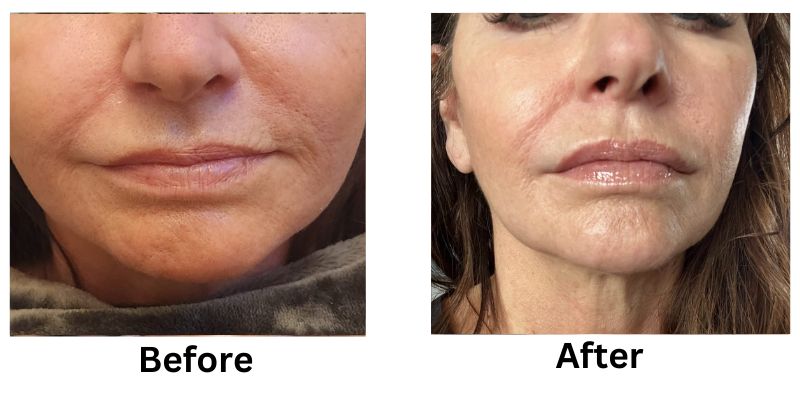
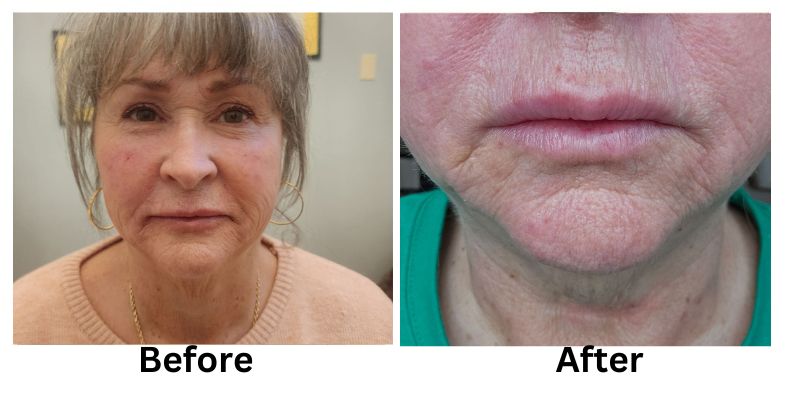
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Lip-Filler-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Lip-Filler-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Before-1-150x150.jpg)
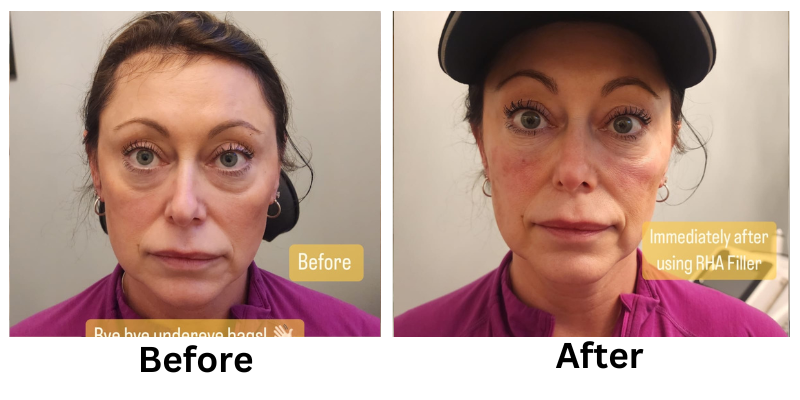


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHA-Treatmetn-1-150x150.png)
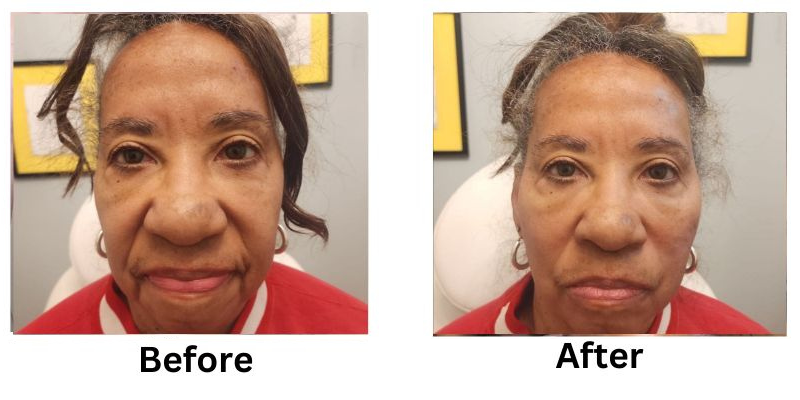

![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Thread-Lifts-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Thread-Lifts-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Lip-Filler-2-150x150.png)

![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/skin-reuvulation1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/skin-rejuvulation-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Skin-Tighting-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before-150x150.jpg)
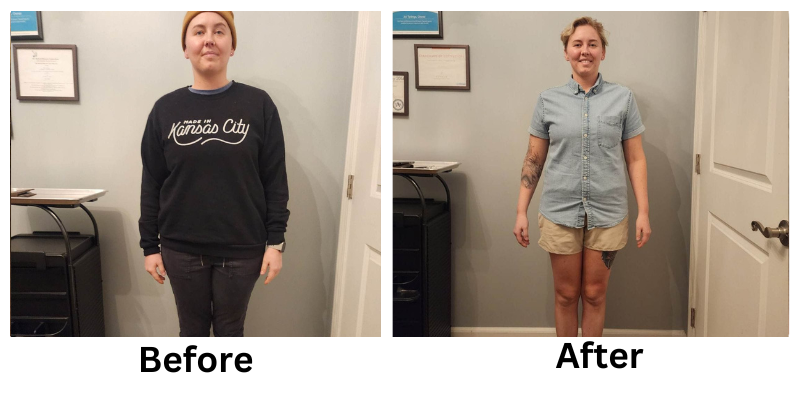
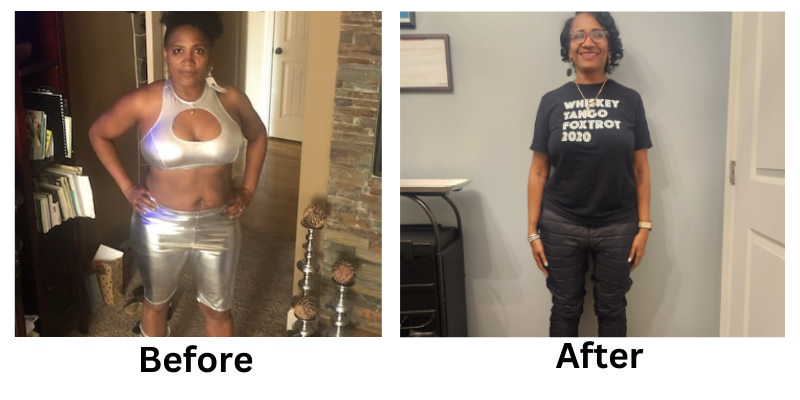
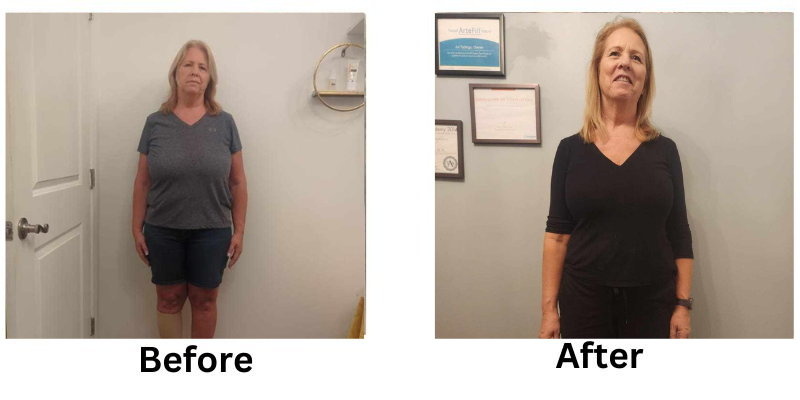



![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/weightloss-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/weightloss-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/2Weight-Loss-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Weight-Loss-1-new-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Weight-Loss-3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Slimming-Solutions-BA-Template-150x150.png)


![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat3-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat-0-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/dat-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Before-1-150x150.png)

![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-2-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-1-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ems-BNA-front-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/EMS-bna-SIDE-150x150.png)
![[thumb]](https://slimmingsolutionsspa.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/EMS-Treatment-6-150x150.png)